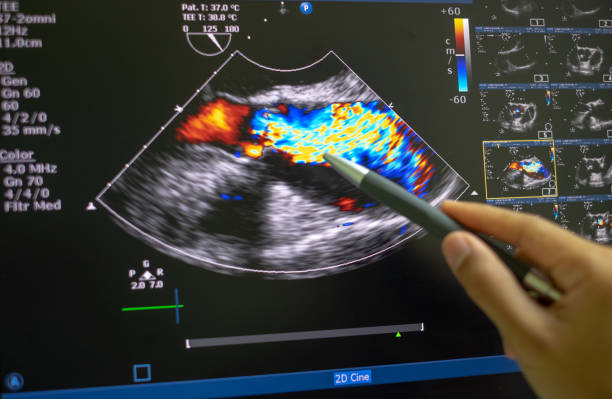
Color Doppler imaging is a specialized ultrasound technique that adds color to the standard grayscale ultrasound images to visualize blood flow within the body. Here’s how it works and its applications in the human body:
- How Color Doppler Works:
- Like traditional ultrasound, Color Doppler uses high-frequency sound waves emitted from a transducer.
- As the sound waves encounter moving blood cells within blood vessels, they undergo a change in frequency (Doppler effect).
- The Color Doppler technique detects these frequency changes and assigns colors to the blood flow based on direction and speed.
- Typically, flow towards the transducer is represented in red, while flow away from the transducer is represented in blue. Turbulent flow may be displayed as other colors, such as green or yellow.
- Applications in the Human Body:
- Cardiac Imaging: Color Doppler is used to assess blood flow through the heart chambers, valves, and major vessels, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions such as valve regurgitation, stenosis, and congenital heart defects.
- Vascular Imaging: Color Doppler is valuable for evaluating blood flow in arteries and veins throughout the body, helping to diagnose conditions such as arterial stenosis, venous thrombosis, and aneurysms.
- Obstetrics and Gynecology: In obstetrics, Color Doppler can assess blood flow in the umbilical cord, placenta, and fetal vessels, providing information about fetal well-being and detecting abnormalities such as placental insufficiency. In gynecology, it can evaluate blood flow in ovarian and uterine vessels, aiding in the diagnosis of ovarian cysts, fibroids, and tumors.
- Abdominal Imaging: Color Doppler is used to assess blood flow in the liver, spleen, kidneys, and other abdominal organs, assisting in the diagnosis of conditions such as portal hypertension, liver cirrhosis, and renal artery stenosis.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: Color Doppler can help evaluate blood flow in joints, muscles, and soft tissues, aiding in the diagnosis of inflammatory conditions, synovitis, and tendon injuries.
- Breast Imaging: In breast ultrasound, Color Doppler can assess blood flow within breast masses, providing additional information to help differentiate between benign and malignant lesions.
- Advantages of Color Doppler:
- Real-time Visualization: Color Doppler provides real-time images of blood flow dynamics, allowing for immediate assessment and interpretation by healthcare providers.
- Non-invasive: Color Doppler is a non-invasive imaging technique that does not require contrast agents or exposure to ionizing radiation, making it safe and well-tolerated by patients.
- High Sensitivity: Color Doppler has high sensitivity for detecting blood flow, even in small vessels or slow-flowing regions, enhancing its diagnostic utility.
- Complementary to Grayscale Imaging: Color Doppler can be used in conjunction with grayscale ultrasound imaging to provide comprehensive diagnostic information about tissue structure and blood flow patterns.
Overall, Color Doppler imaging is a valuable tool in medical practice for evaluating blood flow within the body, aiding in the diagnosis and management of a wide range of medical conditions across various medical specialties